
*Corresponding Author: Syeda Sadiya Ikram, 2Department of Ophthalmology, Saveetha Medical College & Hospital.
Received Date: November 17, 2022
Accepted Date: February 16, 2023
Published Date: March 06, 2023
Citation: Narmadha.R, Syeda Sadiya Ikram and Sanjeev Kumar Puri. (2023) “Comparison of Accommodative Facility and Vergence Facility with and without Myopia”, Ophthalmology and Vision Care, 3(1); DOI: http;//doi.org/03.2023/1.1036
Copyright: © 2023 Syeda Sadiya Ikram. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Aims:
To compare accommodation facility and vergence facility between myopia and emmetropia.
Methods and Material:
This study was done on 50 subjects, age group between 18-30 years.It was a hospital-based comparative study conducted in the outpatient department of Ophthalmology and was approved by the IRB committee.This study has been done to compare the values of accommodative facility and vergence facility between myopic and emmetropic patients.
Results:
It was confirmed that the Accommodative facility [Distance and Near] in right eye, left eye, and both eye was observed as significantly lesser in Myopic patients than the Emmetropia. Also, the Vergence facility was observed as significantly lesser in Myopic patients than the Emmetropic patients.
Conclusions:
A reduced accommodative facility and vergence facility was found in myopes in comparison to emmetropia. At both distance and near, the mean facility was less for myopic eyes in comparison with emmetropic eyes.
Introduction:
Accommodation is the ability of the eye to change focus from one object to another and to maintain the clear focus of the object¹.The accommodative facility tests the speed of accommodative step response². Convergence is a disjugate movement and the ability to turn both eyes inward together to look at a close object. It is an important part of binocular vision testing³. In normal binocular vision, accommodation and vergence co-operate to place on the fovea of each eye a sharp image of the object of regard. The accommodative and vergence facility is a useful predictor of visual discomfort and also academic success.
Subjects and Methods:
This comparative study was done among 50patients [100 eyes] include both males and females.before the beginning of this study informed written consent has given and the procedure has been explained clearly. The patients with the age group of 18-30 were taken into this study. The inclusion criteria include emmetropic and refractive error patients were included and a cylindrical component of less than 1.00D was included. presbyopic patients, cataracts, and squint patients were excluded. This study has been done to compare the values of accommodative facility and vergence facility between myopic and emmetropic patients. The accommodative facility was measured using accommodative manual flippers. It is a holder of a +2.00D lens and a -2.00D lens. It was done on both monocularly and binocularly for each subject at 3m and 40cm. The flipper lens was changed from plus to the minus and back again to the plus. This indicates one cycle. Vergence facility was measured using vergence flippers. It is a holder of 12 prism base out and 3 prism base in prisms. The patient is asked to keep the vergence flipper close to the eyes [base in prism first] and flip the prisms when the print becomes single and clear. It was done binocularly at 40cm. The normal values for the accommodative facility for both distance and near [monocularly] are 11CPM [cycle per minute] and for binocularly is 15CPM. The normative value for vergence facility [binocularly] is 15 CPM.
Results:
|
|
N |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Mean |
Std. Deviation |
|
Age |
50 |
17 |
29 |
21.70 |
2.808 |
Table 1: Descriptive statistics for Age
Comparison Of Myopic And Emmetropic Subjects With Respect To Accommodative Facility [Distance] OD, OS & OU:
In this study, 25 subjects with Myopia and another 25 Emmetropic patients were included in this study. Accommodative facility (Distance) OD, OS & OU of 50 subjects was recorded. This section presents the comparison of Myopic and Emmetropic subjects with regard to Accommodative facility (Distance) OD ,OS & OU. To find the significant difference among the Myopic and Emmetropic subjects with regard to Accommodative facility, Independent Sample t-test is applied. The results are shown in the Table-2.
|
|
|
Mean |
S.D |
t value |
|
Accommodative facility (Distance) OD |
Emmetropia |
15.56 cpm |
3.742 |
7.531** (p = .000) |
|
Myopia |
9.24 cpm |
1.899 |
||
|
Accommodative facility (Distance) OS |
Emmetropia |
15.40 cpm |
4.031 |
6.961** (p = .000) |
|
Myopia |
9.36 cpm |
1.604 |
||
|
Accommodative facility (Distance) OU |
Emmetropia |
17.36 cpm |
3.094 |
7.502** (p = .000) |
|
Myopia |
11.76 cpm |
2.087 |
Table 2: Emmetropic and Myopic Patients with respect to Accommodative Facility [Distance] OD, OS & OU
Source: Computed from Primary data
From the Table-3, the t-value of OD:7.531 (p=.000) ,OS:6.961 (p =.000) & OU:7.502 (p=.000) confirms that there is significant difference observed between subjects with Myopia and Emmetropic subjects with respect to Accommodative facility (Distance) OD, OS & OU. Further the mean Accommodative facility (Distance) OD, OS & OU observed in Myopic subjects (9.24 CPM), (9.36 CPM) & (11.76 CPM) respectively is significantly lesser than the mean Accommodative facility (Distance) OD observed in Emmetropic subjects (15.56 CPM),(15.40 CPM) & (17.36 CPM) respectively. This shows that Accommodative facility (Distance) OD is observed as significantly lesser in Myopic patients than the Emmetropic subjects. The comparison is shown graphically in Figure-3
.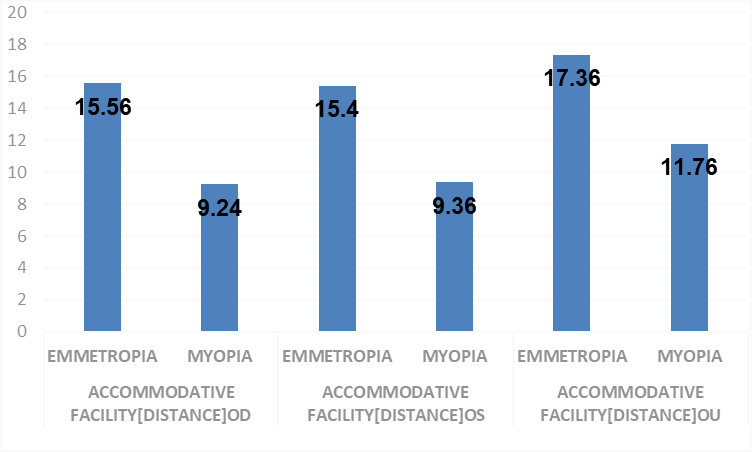
Figure 1: Emmetropic And Myopic Patients Mean Values With Respect To Accommodative Facility [Distance] OD, OS & OU
Comparison Of Myopic And Emmetropic Subjjects With Respect To Accommodative Facility[Near] OD, OS & OU:
This section presents the comparison of Myopic and Emmetropic subjects with regard to Accommodative facility (Near) OD, OS & OU. To find the significant difference among the Myopic and Emmetropic subjects with regard to Accommodative facility, Independent Sample t-test is applied. The results are shown in the Table-3.
|
|
|
Mean |
S.D |
t value |
|
Accommodative facility (Near) OD |
Emmetropia |
15.44 cpm |
3.548 |
7.654** (p = .000) |
|
Myopia |
9.32 cpm |
1.842 |
||
|
Accommodative facility (Near) OS |
Emmetropia |
15.96 cpm |
3.284 |
8.703** (p = .000) |
|
Myopia |
9.68 cpm |
1.492 |
||
|
Accommodative facility (Near) OU |
Emmetropia |
17.88 cpm |
2.976 |
7.952** (p = .000) |
|
Myopia |
12.44 cpm |
1.685 |
Table 3: Emmetropic And Myopic Patients With Regard To Accommodative Facility [Near] OD, OS & OU
Source: Computed from Primary data
From the Table-3, the t-value of OD:7.654 (p=.000), OS:8.703(p=.000) & OU:7.952(p=.000) confirms that there is significant difference observed between subjects with Myopia and Emmetropic subjects with respect to Accommodative facility (Near) OD, OS & OU . Further the mean Accommodative facility (Near) OD, OS & OU observed in Myopic subjects(9.32 CPM), (9.68 CPM) & (12.44 CPM) respectively is significantly lesser than the mean Accommodative facility (Near) OD, OS & OU observed in Emetropic subjects (15.44 CPM), (15.96CPM) & (17.88CPM ) respectively . This shows that Accommodative facility (Near) OD is observed as significantly lesser in Myopic patients than the Emmetropic subjects. The comparison is shown graphically in Figure-2.
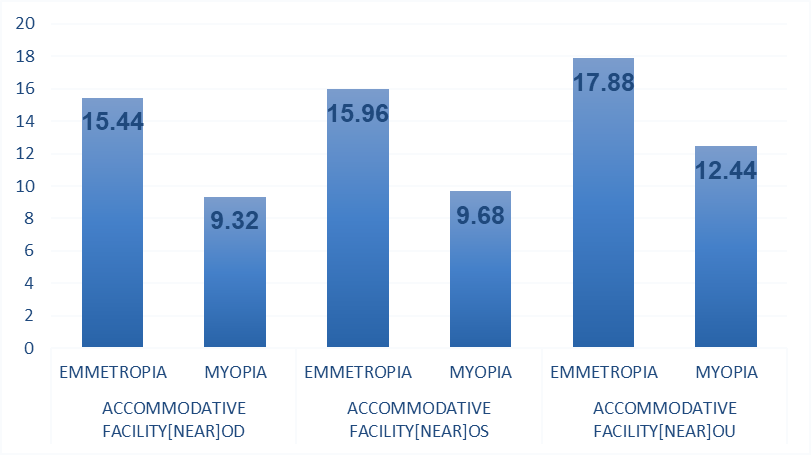
Figure 2: Emmetropic And Myopic Patients Mean Values With Regard To Accommodative Facility [Near] OD, OS & OU
Comparison Of Myopic And Emmeropic Subjects With Respect To Vergence Facility (OU):
In this study, 25 subjects with Myopia and another 25 Emmetropic patients were included in this study. Vergence Facility of 50 subjects was recorded. This section presents the comparison of Myopic and Emmetropic subjects with regard to Vergence Facility. To find the significant difference among the Myopic and Emmetropic subjects with regard to Vergence Facility, Independent Sample t-test is applied. The results are shown in the Table-4.
|
|
|
Mean |
S.D |
t value |
|
Vergence Facility (OU) |
Emmetropia |
17.60 cpm |
2.327 |
8.379** (p = .000) |
|
Myopia |
12.12 cpm |
2.297 |
Table 4: Emmetropic And Myopic Patients With Regard To Vergence Faciliy (OU)
Source: Computed from Primary data
From the Table-4, the t-value of OU:8.379 (p=.000) confirms that there is significant difference observed between subjects with Myopia and Emmetropic subjects with respect to Vergence Facility. Further the mean Vergence Facility observed in Myopic subjects (12.12CPM) is significantly lesser than the mean Vergence Facility observed in Emmetropic subjects (17.6CPM). This shows that Vergence Facility is observed as significantly lesser in Myopic patients than the Emmetropic subjects. The comparison is shown graphically in Figure-3.
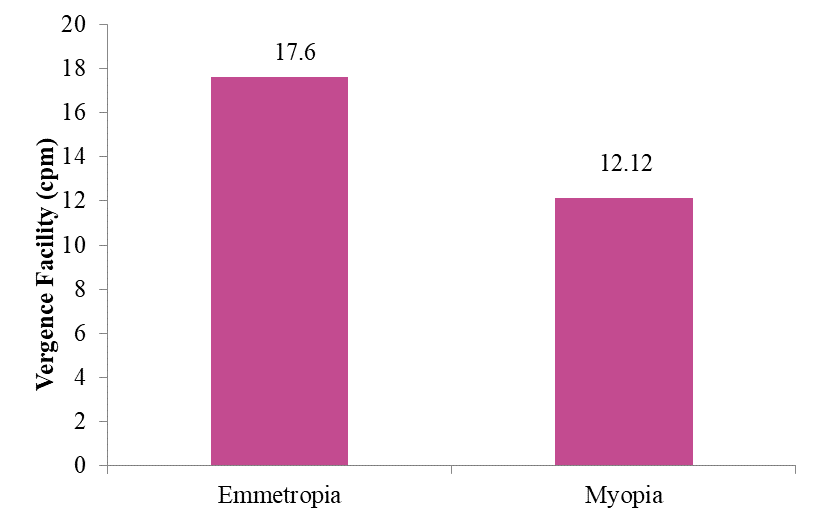
Figure 3: Emmetropic And Myopic Patients Mean Values With Regard To Vergence Faciliy (OU)
Discussion:
Accommodation is the ability of the eye to change focus from one object to another and to maintain a clear focus on the object. Myopia has been found to have abnormal amplitude of accommodation and an abnormal response to blur.4 There is a low ability to accommodate through minus lenses; it seems that accommodative facility can be reduced, at least for part of the facility of the cycle. Accommodative Facility evaluates the speed of accommodative step response. Patients with a history of headache, blurring of vision and asthenopia symptoms often have low flipper rates [accommodative in facility] and inadequate accommodation [accommodative insufficiency]. In normal binocular vision, accommodation and vergence co-operate to place on the fovea of each eye a sharp and clear image of the object of regard¹. O’Leary and Allen et.al [2001]5 study results show that myopes have lower accommodative distance facilities in comparison to emmetropia. Radhakrishnan et.al [2007] 6suggested that the presence of mid-spatial frequencies on the retina denies the need for the accommodative response.In this study, we sought to determine that there was a depression of the accommodative and vergence response in myopic adults in comparison to the response of emmetropic patients. In myopic patients, the accommodative responsiveness to both positive and negative lens defocus was slow when compared to emmetropes.